

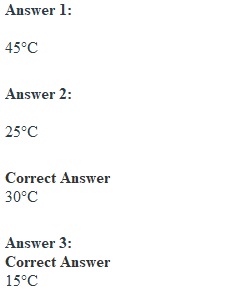
Q Question 1 2.5 / 5 pts Results: I. Effects on Growth To test the growth of E. coli at different temperatures, you inoculated 5 nutrient broths, but forgot to label each inoculated test tube with the appropriate incubation temperatures 15°C, 25°C, 30°C, 37°C, 45°C. After inoculating the unlabeled tubes, you placed each one in the correct incubator or refrigerator. You can clearly observe the turbidity as a sign of growth. After incubation for 24 hours, you take them all out and place them on a test tube rack, and quickly realize that they're unlabeled and you don't know which one came from which temperature. To figure out what their incubation temperatures you figure out a range of growth from no turbidity (-) to high turbidity (++++). You can use the graph included for reference. The 5 tubes are shown below: Understanding that E. coli is a mesophile that resides in the intestines of many mammals, match each tube with the correct incubation temperature. • o Tube A was incubated at ["", "", "", "", ""] o Tube B was incubated at ["", "", "", "", ""] o Tube C was incubated at ["", "", "", "", ""] o Tube D was incubated at 15°C o Tube E was incubated at 30°C Based on these results and your conclusions: Which one is the optimum temperature for growth of E. coli? ["", "", "", "", ""] Which temperature most likely killed E. coli? ["", "", "", "", ""] Which temperature slowed down significantly the growth of E. coli? ["", "", "", "", ""] II. Effects on Pigment Production Understanding the reasons why Serratia marcescens pigment production is temperature dependent, look at the pictures below and match the growth appearance with the correct incubation temperature. • o Tube F was incubated at ["", ""] o Tube G was incubated at ["", ""]
View Related Questions